Connecting to a Data Source
An application will use the connection handle it allocated in order to connect to an RaimaDB data source, by calling SQLConnect(). In SQL API, an RaimaDB data source is a transaction file server (rdm-tfs) that manages one or more databases. The RaimaDB data source can be local to the application or can be accessed remotely. Using a local connection to the RaimaDB data source, SQL API uses the RaimaDB SQL Engine linked to it in order to interact with the target rdm-tfs. On a remote connection, SQL API uses a built-in remote procedure call (RPC) layer to communicate with an rdm-tfs which has its own RaimaDB SQL Engine that in turn processes the requests.
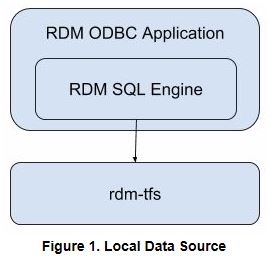
A typical SQL API application is illustrated in Figure 1 below. The application will connect to the default TFS and the SQL processing will be performed within the application process.
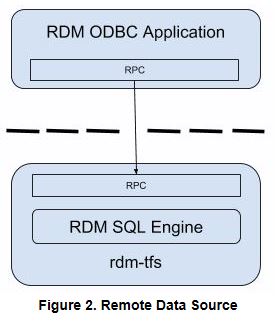
Alternatively, an SQL API application can use its RPC mechanism to connect to a remote rdm-tfs which has its own built-in RaimaDB SQL Engine to process the application's requests (Figure 2). This is a client/server configuration that allows multiple SQL API applications, including third-party ODBC tools, to simultaneously access a single rdm-tfs.