Using CMake for GHS INTEGRITY Cross-Compile
Prerequisites
It is assumed that the GHS INTEGRITY development environment is installed on your machine and available in the path to be found by the CMake tool. It also assumed that the access to the GHS license server is available through the GHS_LMHOST environment variable in the terminal window prior to running CMake.
Prebuilt RaimaDB Cross Targets
The available cross-targets in the RaimaDB installation package can be found in the root directory of the installed package. For example, the Linux hosted GHS INTEGRITY cross-target installer contains one or more targets, as show below:
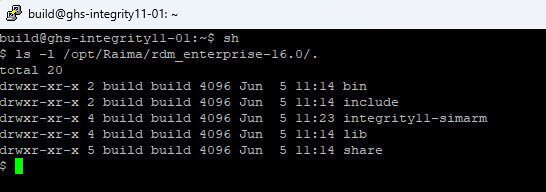
The cross-target directories will typically be named similar to the intended target architecture and will not be one of the directories already described in the Installation Directory Layout.
All cross-targets will contain an identical layout of a bin and lib directory. The lib/cmake/RDM directory contains the toolchain.cmake for building as well as CMake support files. The preset.json file contains information on how the RaimaDB libraries for this target were built.
Building the GettingStarted/c-core/core01Example
The following steps can be applied to any of the C or C++ examples.
- Create a "build" directory and make the new directory the current directory.
$ mkdir mybuild $ cd mybuild
- Run the CMake configuration for the cross-target of your choice. This is done by using the predefined
toolchain.cmakefor
$ cmake -G "Unix Makefiles" -Wno-dev -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=/opt/Raima/rdm-<package>-16.0//<cross-target-directory>/lib/cmake/RDM/toolchain.cmake /opt/Raima/rdm-<package>-16.0//share/RDM/GettingStarted/c-core/core01Example
For example, the following will build the core01Example example for an ARM Simulator using the rdm_enterprise package.
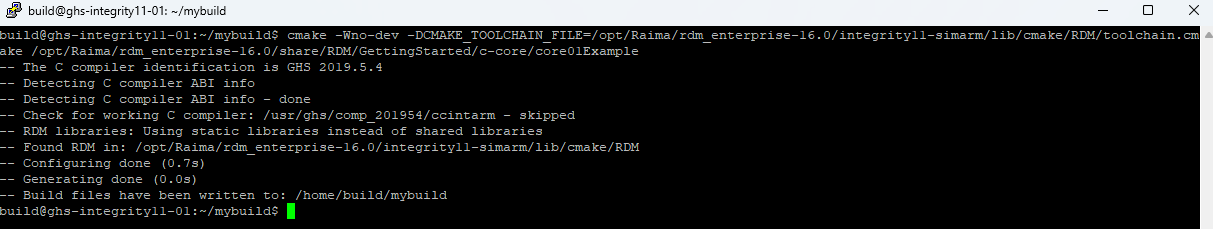
- Assuming no errors on the CMake configuration, the executable can be generated with:
$ make
or
$ cmake --build .
Below is the console out put from building the ARM Simulator configuration from above:
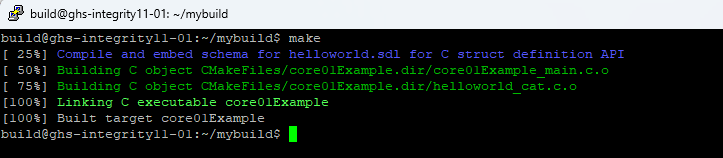
The default for RaimaDB cross-targets is STATIC builds. The resulting executable from the build can be copied to the target hardware and executed without needing to copy additional libraries.